Is sugar addictive? This intriguing question has sparked considerable debate among nutritionists and researchers alike. While substances like alcohol and nicotine are recognized as addictive by clinical standards, the relationship between sugar and addiction remains complex. Many individuals experience strong cravings for sugar and have reported withdrawal-like symptoms when they reduce sugar consumption, shedding light on potential sugar addiction. However, it is essential to understand that sugar exists naturally in many foods, and moderation is key to maintaining a healthy diet without severe psychological or health risks associated with high sugar consumption.
When exploring the topic of sugar and its potential for addiction, various terms like sweet cravings, sugar dependency, and the physiological impacts of sweeteners come into play. Many people find themselves drawn to sugary treats, often thinking about them throughout the day, which raises important questions about dietary habits. These sweet cravings can lead to excess sugar intake, which is linked to numerous health risks. Though sugar consumption is commonplace and necessary in moderation, it is crucial to adhere to established sugar consumption guidelines to avoid the adverse effects of overindulgence. Understanding these various aspects helps illuminate the nuanced discussion surrounding sugar’s role in our diets.
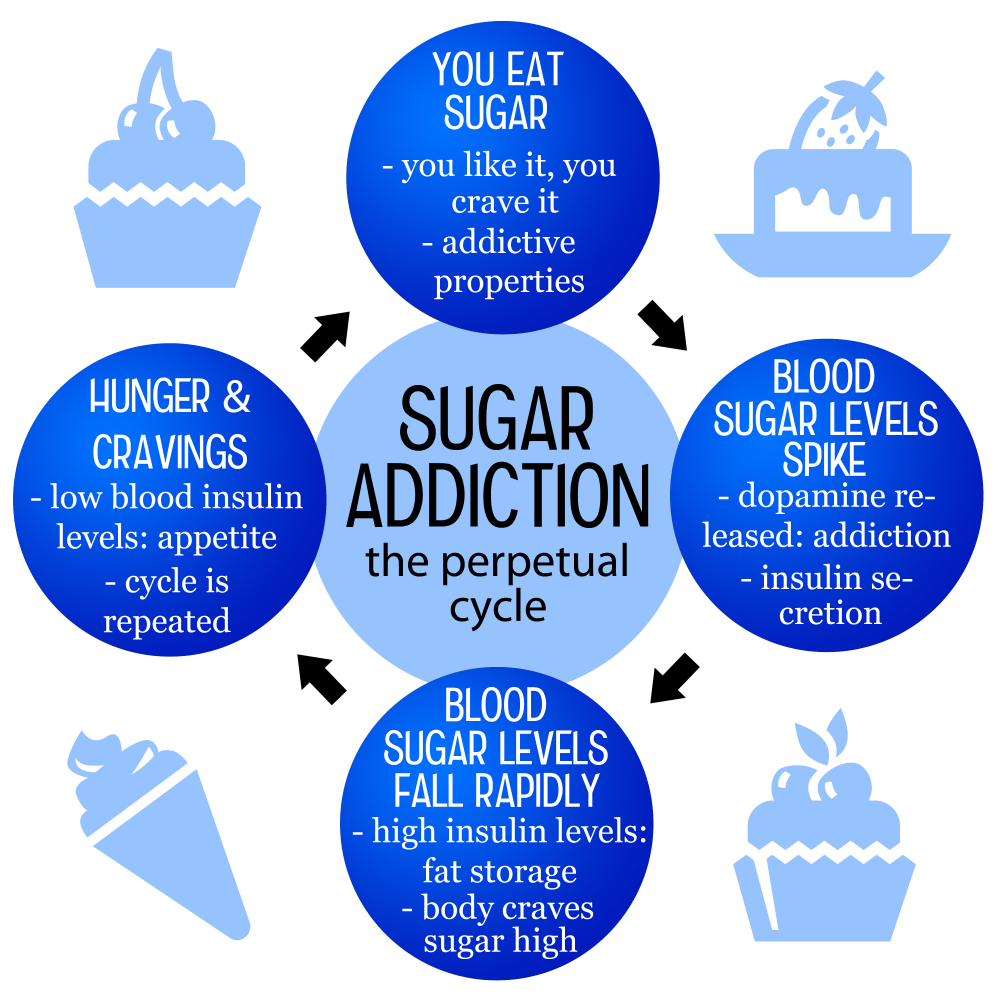
Understanding Sugar Addiction
The question ‘Is sugar addictive?’ has sparked intense debate among nutrition experts and health professionals. While it’s clear that sugar can lead to cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, the classification of sugar as an addictive substance is complex. Unlike substances such as alcohol and nicotine, which meet clinical criteria for addiction due to their withdrawal symptoms and compulsive consumption, sugar does not fit neatly into this framework. However, the psychological effects of consuming high amounts of sugar, especially from ultra-processed foods, can mimic addictive-like behaviors. This results in habitual consumption patterns that are hard to break.
Nutrition researcher Frank Hu from Harvard highlights that while sugar isn’t classified as addictive in the same vein as drugs, individuals can experience withdrawal-like symptoms when reducing their intake. These symptoms may include headaches, anxiety, and cravings, primarily caused by a sudden stop of consuming high-sugar processed foods. This suggests that while sugar can trigger cravings similar to those experienced by addicts, it ultimately is a necessary nutrient when consumed in moderation, complicating our understanding of its potential addictive qualities.
The Effects of Sugar on Health
Consuming excessive amounts of sugar can lead to a host of negative health effects, ranging from obesity to diabetes and heart disease. The average American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, which far exceeds the American Heart Association’s recommendations of 6 to 9 teaspoons for most adults. This overconsumption can cause significant health risks due to the excess calories and lack of nutritional value in sugary foods, leading to obesity and metabolic syndrome.
Moreover, the physiological response to sugar consumption includes spikes in blood sugar levels, which can trigger increased cravings and a cycle of sugar highs and lows. The health risks of sugar extend beyond weight gain; they encompass chronic conditions that impact overall health and quality of life. Being aware of added sugar in your diet and adhering to recommended consumption levels can significantly mitigate these health risks.
Cravings for Sugar: Understanding Triggers
Cravings for sugar are not merely a result of a sweet tooth; they are often influenced by emotional and environmental triggers. Many people reach for sugary snacks during stress or fatigue, which can give a temporary boost in mood or energy. This can make it feel as though sugar has an addictive quality because individuals may continue to seek that quick emotional fix provided by sweet foods. This cyclical behavior reinforces habitual consumption and can lead to a pattern of reliance on sugar for coping.
Additionally, our food environment plays a significant role in these cravings. The prevalence of ultra-processed foods laden with sugar makes it easier to consume larger quantities unconsciously. These products are designed to be highly palatable, further enhancing the desire for sugary treats. Understanding these triggers can help individuals better manage their cravings and make more intentional choices about sugar consumption.
Health Risks of Excessive Sugar Consumption
The health risks of consuming high levels of sugar are significant and alarming. Regular intake of added sugars is associated with an increased risk of various chronic diseases, including type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers. The American Heart Association has set recommended limits for sugar consumption specifically to combat these growing health concerns. Awareness of the detrimental effects of excess sugar is essential in advocating for healthier dietary choices and preventing related health issues.
In addition to chronic diseases, excessive sugar consumption can also impact mental health. High sugar intake has been linked to mood disorders, including anxiety and depression. This connection between sugar and mental health underlines the importance of monitoring our diets to maintain overall wellness. A comprehensive understanding of the health risks associated with high sugar intake is crucial for anyone looking to improve their health or manage conditions exacerbated by sugar.
Guidelines for Sugar Consumption
To mitigate the health risks associated with high sugar intake, following established sugar consumption guidelines is crucial. The American Heart Association suggests that men limit themselves to no more than 9 teaspoons of added sugar per day and women to 6 teaspoons. For children, even lower intake guidelines are recommended. These benchmarks serve as a foundation for making informed dietary choices and help ensure that sugar is enjoyed in moderation rather than excess.
Label reading is an important skill for anyone looking to manage their sugar intake effectively. By being aware of the sugar content in processed foods and beverages, individuals can make more educated choices that align with the recommended guidelines. As people aim to cut back on added sugars, gradual reductions can often be more sustainable than sudden cut-offs, reducing the risk of withdrawal symptoms and cravings.
The Role of Sugar in a Balanced Diet
Despite the negative connotations surrounding sugar, it’s important to remember that sugar, in moderation, plays a role in a balanced diet. Naturally occurring sugars found in fruits, vegetables, and dairy products come with essential nutrients and fiber, contributing positively to our overall health. Instead of fearing sugar altogether, understanding how to incorporate it wisely into a healthy eating plan can help create a more enjoyable and satisfying diet.
For individuals struggling with intense cravings for sugar, finding healthier alternatives can be a beneficial approach. Incorporating whole fruits as a sweet snack or opting for unsweetened dairy can provide the sweetness one desires without overwhelming the body with added sugars. A mindful approach to sugar consumption can enhance flavor and satisfaction while still adhering to health guidelines.
Managing Sugar Cravings Effectively
Managing cravings for sugar effectively requires a proactive approach. One method is to identify triggers that lead to sugar consumption, whether emotional stress or habitual eating patterns. When individuals can pinpoint these triggers, they can create strategies to address the underlying causes rather than succumbing to cravings. This may involve incorporating more whole foods into meals, practicing mindful eating, or maintaining regular meal schedules to stabilize blood sugar levels.
Additionally, having healthy snacks available can reduce the temptation to reach for sugary treats. By preparing snacks that are high in fiber and protein, individuals can feel fuller for longer and curb their cravings for sugar. Emphasizing the importance of preparation and awareness can help people take control of their sugar intake and reduce the frequency and intensity of cravings.
The Psychological Impact of Sugar
The psychological impact of sugar on our bodies and minds can be profound. Sugar can trigger the release of dopamine in the brain, leading to feelings of pleasure and reward. This response can create a cycle of seeking out sugary foods for comfort or reward, indicating an almost addictive nature of sugar consumption in some contexts. Understanding this psychological relationship can help individuals navigate their dietary choices more effectively.
Conversely, becoming overly restrictive about sugar can also lead to negative psychological consequences, such as binge eating or intense cravings. It is crucial to find a balance between enjoyment and moderation. Recognizing that sugar can be part of a healthy lifestyle when consumed mindfully can alleviate the guilt often associated with sugar consumption. This understanding allows for a more positive relationship with food overall.
The Future of Sugar Consumption Research
Research on sugar consumption and its effects is ongoing, with many experts focusing on how sugar addiction parallels traditional addictions like alcohol or drugs. As new studies emerge, we can gain a better understanding of how sugar affects physical and mental health. Furthermore, insights into sugar’s effects can guide public health policies and dietary recommendations aimed at reducing sugar consumption in populations.
As awareness of sugar’s potential health risks grows, there is a push for more comprehensive guidelines surrounding sugar consumption. Ongoing research will play a crucial role in shaping not just individual dietary choices but also larger societal approaches to health and nutrition. Keeping up with the latest studies will be essential for those looking to understand and adapt to the evolving landscape of sugar consumption and its implications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like alcohol or nicotine?
While sugar can increase cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. Sugar does have some addictive qualities, but it mostly depends on the dose and frequency of consumption.
What are the effects of sugar on the body?
Sugar can lead to cravings and a preference for sweet foods, contributing to a cycle of habitual consumption. Excessive sugar intake, particularly from added sugars found in processed foods, can lead to health risks like obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
How can I manage cravings for sugar?
To manage cravings for sugar, gradually reduce your intake instead of going cold turkey. Focus on consuming whole foods and read labels for added sugars. Maintaining a balanced diet can help stabilize blood sugar levels and minimize cravings.
What are the health risks of sugar consumption?
High sugar consumption is linked to numerous health risks such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and dental problems. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar intake to 9 teaspoons for men and 6 teaspoons for women.
What are the sugar consumption guidelines from health authorities?
Health authorities like the American Heart Association suggest limiting added sugar intake to no more than 9 teaspoons (36 grams) per day for men, 6 teaspoons (25 grams) for women, and less for children to promote better health.
Is there a difference between natural and added sugars in terms of addiction?
Natural sugars found in fruits and dairy are generally not associated with cravings and negative health effects like added sugars in processed foods. However, it’s essential to moderate all forms of sugar, focusing on the overall dietary context.
How does sugar lead to withdrawal-like symptoms?
When people cut back on sugar, especially from ultra-processed foods, they may experience withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and anxiety due to the sudden decrease in habitual sugar consumption.
Can I include sugar in my diet without negative health effects?
Yes, moderate sugar consumption can enhance your diet without negative health consequences. Prioritizing natural sources and limiting added sugars can help you enjoy sweetness while maintaining a balanced diet.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Sugar’s Addictiveness | Sugar increases cravings and compulsive behaviors, but isn’t officially classified as addictive like alcohol or nicotine. |
| Physical Effects | Withdrawal-like symptoms from stopping sugar include headaches, dizziness, and anxiety. |
| Comparative Substance Classification | Unlike addictive drugs, some sugar consumption is necessary as it’s present in foods vital for health. |
| Consumption Recommendations | Average U.S. sugar intake is nearly 20 teaspoons daily; recommendations are 9 for men, 6 for women. |
| Gradual Reduction Advice | Rather than going cold turkey on sugar, it’s better to gradually reduce intake. |
| Sugar’s Role in Diet | Sugar can enhance flavor and texture and is necessary for enjoyment in food. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? While some argue that sugar has addictive qualities similar to drugs, it is not classified as an addictive substance according to clinical guidelines. The physical and psychological effects of sugar cravings can be significant, resulting in withdrawal-like symptoms when consumption is halted. However, it is essential to understand that sugar is a common part of many nutritious foods, making moderation the key rather than complete elimination. Balancing sugar intake is crucial, as excessive consumption can lead to health consequences, while a necessary amount can contribute positively to our diets. Ultimately, respecting the role of sugar within a balanced diet can prevent the negative implications of overconsumption.