Age-related brain diseases, including conditions such as stroke, dementia, and late-life depression, pose increasing challenges as populations age. Recent research highlights the importance of modifying risk factors associated with these ailments to enhance mental health and aging. By adopting effective dementia prevention tips and adhering to brain health guidelines, individuals can significantly reduce their risk. Understanding and addressing stroke risk factors is crucial, as many of these diseases share common origins, making proactive management essential. Engaging with strategies for modifying risk factors can lead to a healthier brain and ultimately a better quality of life.
As we delve into the realm of cognitive decline among the elderly, it’s essential to explore conditions that affect mental acuity, such as neurodegenerative disorders and cerebrovascular diseases. The connections between strokes, memory loss, and emotional wellbeing highlight a growing concern in gerontology. Tackling the root causes through lifestyle adjustments and health interventions can not only aid in dementia prevention but also help mitigate the impacts of late-life mental health issues. By identifying shared risk components and promoting healthy activities, we aim to foster a proactive approach to maintaining brain vitality throughout the aging process.
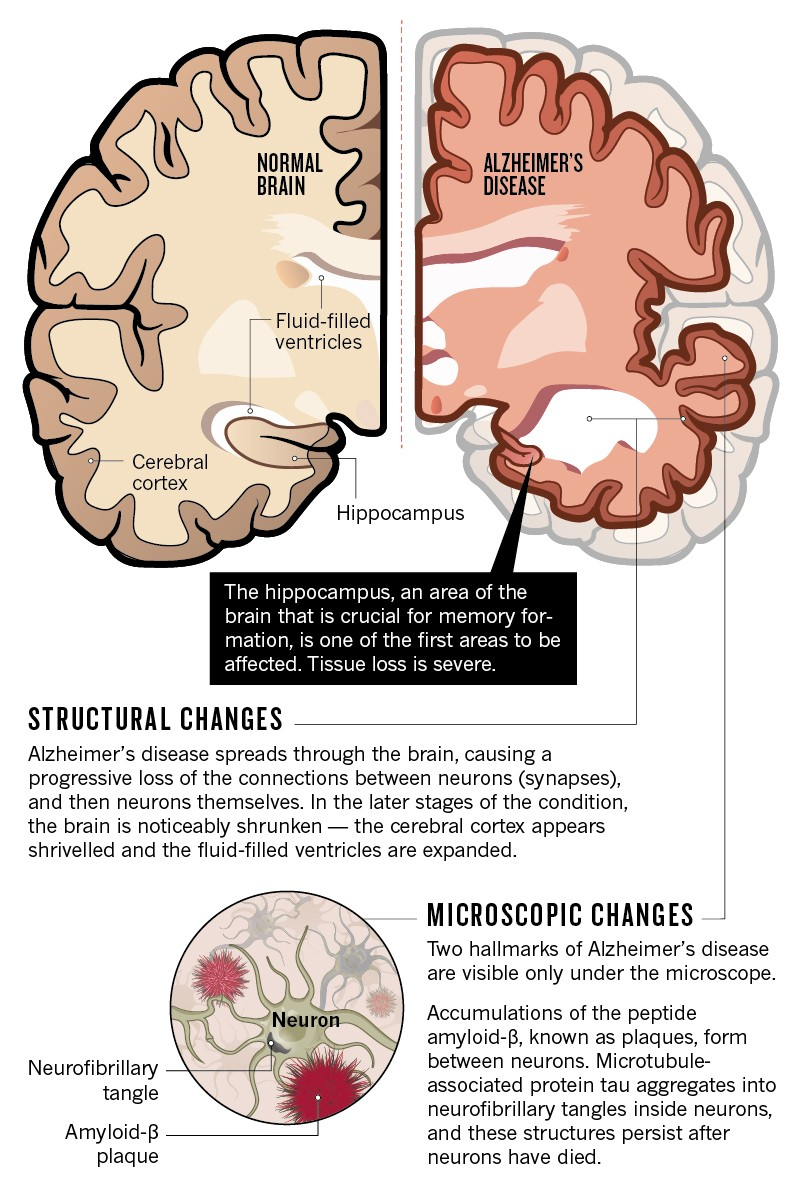
Understanding Age-Related Brain Diseases
Age-related brain diseases, including stroke, dementia, and late-life depression, pose significant challenges to public health, particularly as populations age. These conditions often share common underlying risk factors, making it crucial to understand their interconnections. For instance, high blood pressure is a substantial risk factor that contributes to all three diseases, highlighting the need for comprehensive strategies that address these overlapping health issues.
Addressing age-related brain diseases begins with recognizing how lifestyle choices influence brain health and overall well-being. By implementing healthy habits such as regular physical activity and a balanced diet, individuals can potentially decrease their risk of developing these debilitating conditions. Moreover, fostering strong social connections and managing stress levels can further contribute to mental well-being, illustrating the importance of a holistic approach to brain health.
17 Risk Factors for Age-Related Brain Diseases
Recent research has identified seventeen key modifiable risk factors that significantly affect the likelihood of developing age-related brain diseases. Among these, factors such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and poor diet were found to be critical in influencing the risk of stroke, dementia, and depression. Understanding these risk factors provides valuable insights into how individuals can take actionable steps in modifying their lifestyle to improve brain health.
Additionally, conditions like kidney disease and hearing loss stand out as particularly impactful, suggesting that early detection and management of these issues could lead to improved outcomes. The connection between these risk factors and brain health emphasizes the need for healthcare providers to incorporate brain health guidelines into routine care, thereby fostering an environment where prevention of age-related diseases becomes a priority for patients of all ages.
Dementia Prevention Tips for Healthy Aging
Preventing dementia requires a proactive approach to health and lifestyle. Key strategies include regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet rich in nutrients, and staying mentally stimulated with activities such as puzzles and reading. These practices can lead to significant improvements in brain health and may mitigate risk factors that contribute to dementia development.
Moreover, establishing a supportive social network and minimizing stress through mindfulness or relaxation techniques can enhance mental health as individuals age. Practical tips like prioritizing sleep hygiene and managing blood pressure also play a vital role in dementia prevention. By integrating these strategies into daily routines, individuals can take significant steps toward preserving cognitive function throughout their lives.
Modifying Risk Factors to Enhance Brain Health
Modifying risk factors is essential for enhancing brain health and preventing age-related diseases. Researchers have demonstrated that addressing factors like high cholesterol, obesity, and smoking can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing stroke, dementia, and depression. Initiatives aimed at educating individuals about the importance of these changes can empower them to improve their health outcomes.
Moreover, developing community programs that encourage healthy lifestyle choices, such as exercise groups and nutritional workshops, can facilitate long-term changes. The emergence of tools like the Brain Care Score provides an innovative method for individuals to gauge their brain health and identify areas for improvement, ultimately promoting a proactive stance toward mental health and aging.
Mental Health and Aging: A Vital Connection
The relationship between mental health and aging is intricate, with several factors influencing cognitive decline and emotional well-being. Conditions such as chronic stress, untreated depression, and social isolation can exacerbate changes in mental health as individuals age. Recognizing the signs of declining mental health is crucial for timely intervention and support.
To address these issues, it’s important to create environments that promote mental well-being among older adults. This can include regular mental health screenings, access to counseling services, and the implementation of community activities that foster social engagement. By prioritizing mental health, we can enhance the quality of life for seniors and reduce the risk of developing dementia and other age-related brain diseases.
The Impact of Lifestyle on Brain Diseases
Lifestyle choices play a pivotal role in shaping brain health and determining the risk of developing age-related diseases. Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy diet, and managing stress can lead to significant reductions in the risk factors associated with stroke and dementia. This holistic understanding of lifestyle impacts emphasizes the need for individualized health plans that promote sustainable living.
Furthermore, the integration of cognitive and physical activities into daily routines can foster a more resilient brain. Encouraging activities that challenge the mind while also promoting physical health can create a dual benefit, potentially delaying the onset of cognitive decline. By prioritizing a healthy lifestyle, individuals can take proactive measures in maintaining brain health throughout the aging process.
Social Engagement and Its Role in Brain Health
Social engagement has been linked to improved cognitive function and a decreased risk of mental health conditions in older adults. Regular interactions with peers can provide emotional support, reduce feelings of loneliness, and stimulate mental activity, all of which are beneficial for brain health. Communities that foster social connections by organizing group activities can greatly enhance the mental health of their older residents.
Additionally, meaningful social engagement can serve as a protective factor against age-related brain diseases. Individuals involved in community service or social groups often report a greater sense of purpose and reduced stress, both of which contribute positively to mental health. Encouraging older adults to remain active participants in their communities can be a powerful strategy in preventing the onset of conditions like dementia and depression.
Combating Stress as a Risk Factor
Chronic stress is a significant risk factor for the development of age-related brain diseases, including stroke and dementia. Understanding the impact of stress on mental health is crucial for effective intervention strategies. Learning stress management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and yoga can greatly benefit older adults by reducing their overall stress levels, thereby lowering the risk of developing these conditions.
Moreover, healthcare professionals should educate patients about the detrimental effects of prolonged stress and encourage them to adopt coping strategies that promote resilience. Community programs that offer stress-reduction workshops or support groups can provide additional resources and support for older adults facing high levels of stress, contributing to their overall cognitive health.
The Role of Nutrition in Brain Health
Nutrition is a foundational element of brain health, with certain dietary patterns linked to a reduced risk of age-related diseases. Diets rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and whole grains have been shown to contribute to better cognitive function and reduced inflammation. By emphasizing the importance of nutrition, we can empower individuals to make informed choices that positively affect their brain health.
Furthermore, educational initiatives aimed at promoting healthy eating habits can improve not just individual health outcomes but also community wellbeing. Meal planning, cooking classes, and nutritional workshops can facilitate healthier eating decisions, which have the potential to minimize the risk factors associated with dementia and other related diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main stroke risk factors associated with age-related brain diseases?
The primary stroke risk factors associated with age-related brain diseases include high blood pressure, diabetes, kidney disease, and obesity. Modifying these factors through lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of stroke as well as dementia and late-life depression.
How can dementia prevention tips help in reducing the risk of age-related brain diseases?
Dementia prevention tips such as maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress can help lower the risk of age-related brain diseases. By promoting brain health through these behavioral changes, individuals can decrease their likelihood of developing dementia, stroke, and depression.
What role do modifying risk factors play in preventing age-related brain diseases?
Modifying risk factors, such as controlling blood pressure, reducing alcohol intake, and increasing social engagement, plays a crucial role in preventing age-related brain diseases. By addressing these modifiable factors, individuals can enhance their brain health and potentially prevent conditions like stroke and dementia.
How does mental health and aging relate to the risk of developing brain diseases?
Mental health and aging are closely linked, as poor mental health can exacerbate the risk of age-related brain diseases like dementia and late-life depression. Taking steps to improve mental well-being through activities that foster purpose in life and social engagement can help mitigate these risks.
What are some recommended brain health guidelines to lower the risk of age-related brain diseases?
Recommended brain health guidelines include regular physical exercise, a balanced diet rich in nutrients, adequate sleep, and maintaining social connections. Following these guidelines can help lower the risk of age-related brain diseases, including stroke, dementia, and depression.
| Risk Factor | Impact on Age-Related Brain Diseases |
|---|---|
| Diabetes | Increases risk for stroke, dementia, and depression |
| Blood Pressure | Major risk factor for all three conditions |
| Kidney Disease | Increases risk for stroke, dementia, and depression |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose | High levels linked to increased risk |
| Total Cholesterol | Linked to higher risk of stroke and dementia |
| Alcohol Use | Excessive use increases risk for all conditions |
| Diet | Poor diet contributes to all three conditions |
| Hearing Loss | Modifiable risk factor for dementia |
| Pain | Chronic pain increases risk for depression |
| Physical Activity | Lack of activity is a risk factor for all three conditions |
| Purpose in Life | Lack of purpose contributes to depression |
| Sleep | Poor sleep increases risk for depression |
| Smoking | Major risk factor for all three conditions |
| Social Engagement | Lack of engagement contributes to depression |
| Stress | Chronic stress increases risk for depression |
| Depression | Untreated depression increases risk for other conditions |
| Obesity | Risk factor for stroke, dementia, and depression |
Summary
Age-related brain diseases, including stroke, dementia, and late-life depression, share numerous risk factors that can be modified through lifestyle changes. Recent research from Mass General Brigham highlights 17 specific factors—ranging from blood pressure to diet—that can significantly influence the risk of developing these conditions. By addressing these modifiable risks, individuals can potentially reduce their likelihood of experiencing the burden of these intertwined diseases, emphasizing the importance of proactive health measures.