Suicide prevention for older adults is an essential and pressing issue that often goes unnoticed in mental health discussions. With staggering rates of depression and suicidal tendencies among seniors, especially those aged 75 and older, there is a critical need for targeted mental health resources for seniors. Despite the high senior suicide rates, many reputable organizations have not prioritized this demographic in their online suicide prevention efforts. The gap in healthcare for the elderly can lead to feelings of isolation and despair, further exacerbating their mental health crises. It’s imperative that we develop strategies focused on providing easily accessible resources that cater specifically to the needs of aging individuals, ensuring they receive the support they deserve and preserving their dignity in their twilight years.
Addressing the urgent issue of older adult suicide requires an understanding of geriatric mental health and the societal challenges these individuals face. Many seniors grapple with feelings of loneliness and mental distress that can lead to tragic outcomes, marking them as a vulnerable population desperately needing assistance. Enhancing online suicide prevention resources can bridge this gap and provide much-needed support and intervention. By expanding the focus on the elderly within mental health frameworks, we can implement effective strategies that recognize their unique challenges, such as physical health decline and social isolation. It is vital to create comprehensive strategies that include tailored healthcare services and community programs designed specifically for the aging population.
Understanding the Elevated Suicide Rates Among Older Adults
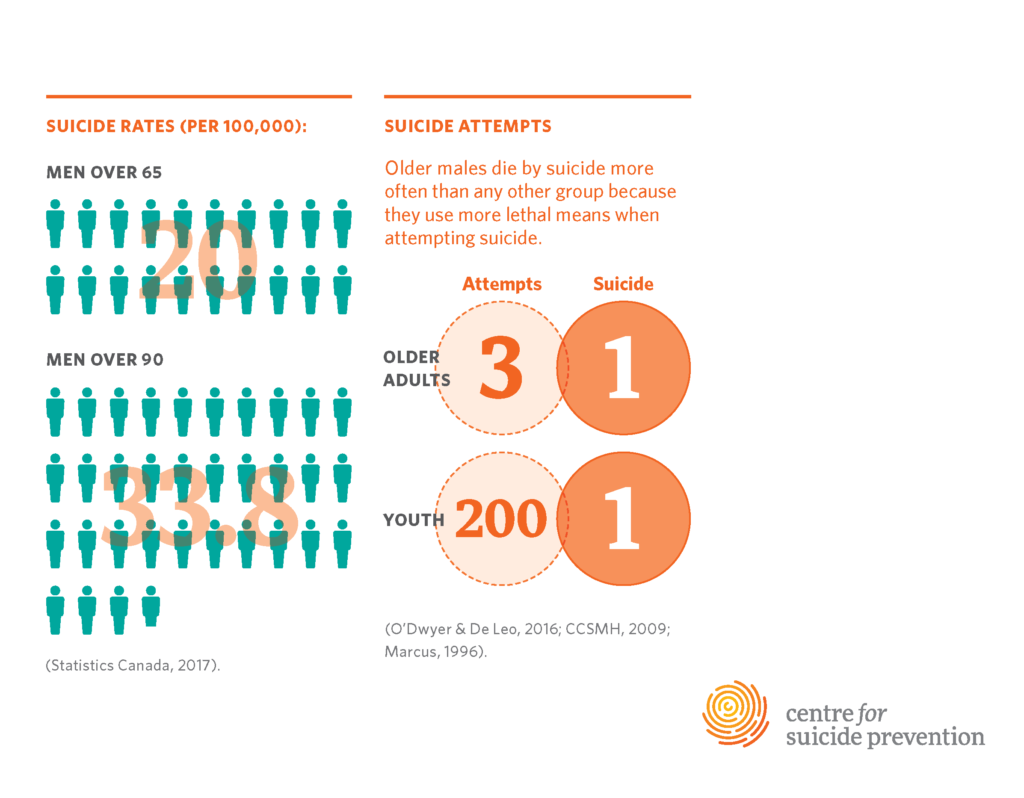
Older adults, especially those aged 75 and older, face alarming suicide rates that surpass any other demographic group. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the suicide rate for this age group is currently at 20.3 per 100,000 individuals, and the trend shows a troubling increase. Factors contributing to this rise include profound social isolation, loneliness, and the systemic biases that often leave the elderly underrepresented in research studies and mental health resources. These challenges render older adults particularly vulnerable, highlighting the urgent need for focused attention on their mental health and well-being.
It is critical to recognize the complexities surrounding geriatric mental health, as older adults frequently grapple with a host of challenges, including the loss of loved ones, chronic health issues, and the transition into retirement. Each of these factors compounds feelings of sadness and hopelessness, which can escalate to suicidal thoughts if not addressed promptly. As communities strive to support seniors, better understanding the struggles that contribute to higher suicide rates is vital. By tailoring mental health resources and suicide prevention strategies specifically for older adults, we can enhance their quality of life and promote mental wellness.
The Need for Tailored Suicide Prevention for Older Adults
Despite the evident need, current suicide prevention efforts largely overlook older adults in their outreach and resource development strategies. Many well-known national organizations fail to provide easily accessible, age-appropriate mental health resources for seniors. This gap in services is profound, given that older adults increasingly turn to online platforms for health-related information. The disconnection between the high risk of suicide in this age group and the relative scarcity of targeted resources lays bare a critical flaw in our healthcare system that must be addressed.
To effectively combat this crisis, it’s imperative that suicide prevention campaigns not only acknowledge the unique experiences of older adults but also leverage online tools that can reach this audience where they are comfortable finding information. Initiatives could be developed that feature relatable content regarding geriatric mental health, community support, and direct pathways to assistance. By creating awareness and improving accessibility, organizations can equip seniors with the resources they need to seek help and ultimately reduce the alarming suicide rates within this population.
Incorporating senior-specific messaging into existing mental health campaigns can also prove beneficial. By normalizing discussions around mental health issues, we can help dismantle stigmas that often prevent older adults from accessing support. Mental health resources for seniors should include information on coping strategies, social support networks, and the importance of reaching out for help, ultimately creating an environment where seeking assistance is encouraged and normalized.
Barriers to Online Suicide Prevention Resources for Seniors
Despite the internet being a growing resource for health information, older adults face significant barriers that hinder their ability to find and access online suicide prevention resources. Many seniors may struggle with navigating complex websites or may not even know which sources are credible. Furthermore, the language and content of many online mental health resources may be overly technical or not resonate with their life experiences, making it difficult for them to engage effectively with the content.
Additionally, the digital divide presents a critical challenge for older adults, as some may lack access to the internet or the necessary devices to seek help online. Public health initiatives must recognize these barriers and work to develop user-friendly platforms that cater to the specific needs of older adults. This can include simplified navigation, options for discussing concerns in familiar terms, and avenues for offline assistance if needed. Improving the accessibility of mental health resources is paramount to ensuring that older adults can find the help they urgently need.
Integrating Mental Health into Healthcare for the Elderly
As we seek to improve mental health resources for seniors, it is essential to integrate these services into the broader healthcare system. Addressing mental health should not be an afterthought; it must be a core component of overall health care for older adults. By cultivating an integrated approach, healthcare providers can screen for mental health issues alongside physical health assessments, thus identifying at-risk individuals earlier in the process.
Moreover, training healthcare professionals in geriatric mental health is crucial in providing comprehensive care. Understanding the unique factors that contribute to mental health challenges in older adults will enable providers to offer timely interventions and appropriate referrals. The synergy between physical and mental health support can foster resilience in this demographic, paving the way for enhanced quality of life, reduced suicide rates, and more effective healthcare outcomes.
Promoting Community Engagement and Support for Seniors
Sustained engagement in community activities can significantly contribute to reducing the risk of suicide among older adults. Isolation is a major factor that exacerbates mental health challenges and can lead to feelings of hopelessness. Community programs that encourage social interaction, such as senior centers, support groups, and volunteer opportunities, can help build strong support systems. These initiatives promote connections, enhance purpose, and allow older adults to share their experiences with others going through similar challenges.
Community-based resources can also provide a direct path to mental health services, making it easier for seniors to seek help when they need it the most. By fostering an environment of support and care, we can engage older adults in meaningful activities that will uplift their spirits and promote mental wellness. Collaborative efforts among local organizations, healthcare providers, and caregivers are essential to create comprehensive support networks that prioritize the mental health of seniors, effectively addressing the imbalances observed in suicide prevention efforts.
The Role of Family in Supporting Elder Mental Health
Family members often play a critical role in identifying the early signs of mental health issues among older adults. This support can be vital in bridging the gap between seniors and the mental health resources they need. Family members should be educated about the signs of depression, anxiety, and suicidal thoughts to ensure that they can respond with compassion and urgency if they notice concerning behavior. Open dialogues about mental health in families can normalize these discussions, making it easier for older adults to express their feelings.
Additionally, families can encourage their elderly relatives to seek help and accompany them to appointments or assist them in navigating online resources. By fostering an atmosphere of trust and care, families can empower older adults to engage with mental health resources. Support from loved ones can significantly influence the willingness of seniors to access help, thereby playing a pivotal role in suicide prevention.
Advocacy for Increased Funding in Elderly Mental Health Research
There’s a pressing need for increased funding dedicated to research aimed at understanding and preventing suicide among older adults. Current statistics highlight a concerning trend, but limited funding hampers the development of effective strategies to combat senior suicide rates. Research focused on geriatric mental health can uncover critical insights into the unique challenges this demographic faces, leading to more informed and effective prevention strategies.
Advocacy for funding can drive attention toward tailoring mental health resources that directly address the needs of older adults. Investing in research can reveal effective online suicide prevention methodologies, helping to bridge the gap in accessibility. Additionally, targeted programs informed by robust research can enhance awareness and outreach, ensuring optimal support systems are in place to reduce the risk of suicide among the elderly.
Utilizing Technology for Online Suicide Prevention Initiatives
Technology presents exciting opportunities for enhancing suicide prevention efforts tailored to older adults. With the increasing comfort level many seniors have with using the internet, online platforms can become effective tools to disseminate information and resources. Initiatives could include online counseling services, interactive webinars about mental health, and easy-to-navigate websites focused on suicide prevention specifically targeting older adults.
By embracing technological innovations, organizations can create vital lifelines for seniors who may not feel comfortable seeking help in a traditional setting. Telehealth options, in particular, allow for flexible access to therapeutic support while reducing the stigma associated with in-person visits. It’s crucial that these online suicide prevention initiatives are designed with user experience in mind to ensure they are inclusive and easily accessible for older populations.
Creating Safe Spaces for Discussing Mental Health Concerns
Establishing safe and welcoming spaces for older adults to discuss mental health is vital for promoting awareness and encouraging usage of available resources. Community centers, support groups, and virtual forums specifically designed for seniors can offer environments where they feel comfortable sharing their experiences. The stigma surrounding mental health needs to be dismantled, and when older adults see their peers talking openly about these issues, it fosters a culture of acceptance and support.
These safe spaces can serve as hubs for mental health education and awareness, paving the way for the dissemination of important information regarding suicide prevention. By integrating mental health discussions into everyday community interactions, we can empower older adults to recognize their challenges and seek help, ultimately lowering the suicide rates in this vulnerable population.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most effective mental health resources for seniors to prevent suicide?
Effective mental health resources for seniors include community support groups, hotlines specifically for older adults, and online suicide prevention platforms that cater to their needs. Local healthcare facilities often provide tailored mental health services that take into account the unique challenges faced by elderly individuals. It’s important for seniors to have access to age-appropriate counseling and support.
What are the suicide rates among older adults and how can they be addressed?
Suicide rates among older adults, particularly those aged 75 and over, are alarmingly high at 20.3 per 100,000. Addressing this issue requires targeted suicide prevention programs that address social isolation, mental health resources for seniors, and awareness campaigns tailored to this demographic. Improving access to healthcare for elderly individuals is crucial for reducing these rates.
How can online suicide prevention resources be optimized for older adults?
Online suicide prevention resources must be designed with older adults in mind, featuring clear navigation, large fonts, and easy-to-understand language. Websites should offer direct links to mental health resources for seniors, highlighting local services and support groups, so older adults can find the help they need quickly and easily.
What role does social isolation play in senior suicide rates?
Social isolation significantly contributes to higher suicide rates among older adults. Many seniors experience loneliness due to loss of loved ones, reduced mobility, or lack of community engagement. Combatting social isolation through community programs, regular check-ins, and support networks can help improve the mental health of elderly individuals and reduce the risk of suicide.
Why do seniors face barriers in accessing suicide prevention resources?
Seniors often face barriers such as technological challenges, lack of awareness about available mental health resources, and systemic biases in healthcare. Many online suicide prevention efforts do not effectively target older adults, which leads to a significant gap in the services tailored for their specific needs. Addressing these barriers involves creating more accessible and relatable support systems.
What preventive measures can be taken to lower suicide rates in the elderly?
Preventive measures to lower suicide rates in the elderly include enhanced training for healthcare providers in geriatric mental health, increased funding for targeted mental health programs, and public awareness campaigns focused on the signs of suicidal ideation in older adults. Connecting seniors with mental health resources and fostering community connections can also be effective.
Where can older adults find urgent mental health resources for suicide prevention?
Older adults can find urgent mental health resources for suicide prevention through local crisis centers, helplines specifically designed for seniors, and community health organizations. Additionally, many online platforms offer immediate support and information about healthcare for elderly individuals, making it easier for them to seek help.
How can families support older adults at risk of suicide?
Families can support older adults at risk of suicide by maintaining open communication, encouraging the use of mental health resources for seniors, and regularly checking in on their emotional wellbeing. Being aware of the signs of mental distress and promoting social engagement can significantly help reduce the risk of suicidal thoughts among elderly family members.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| High Risk of Suicide | Older adults, especially those aged 75 and older, have the highest suicide rates. |
| Lack of Resources | Study shows a scarcity of easily accessible resources aimed at older adults from major suicide prevention organizations. |
| Imbalance in Online Resources | Research indicates that online suicide prevention efforts do not effectively target older adults despite acknowledging their high risk. |
| Need for Targeted Campaigns | There is a need for specific campaigns and programming to address the unique healthcare needs of older adults. |
| Social Isolation as a Factor | Increasing social isolation and loneliness contribute to rising suicide rates among older populations. |
| Call for Action | Researchers urge greater funding and tailored approaches to improve suicide prevention for older adults. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is a critical area that requires immediate attention, as this demographic is experiencing the highest rates of suicide yet has the fewest resources available to them. The recent findings from McLean Hospital underscore the urgent need for targeted campaigns and easily accessible resources that cater specifically to older individuals. Addressing these disparities not only involves recognizing the unique challenges they face, such as social isolation but also implementing effective strategies that engage this population in meaningful ways. By enhancing online accessibility and increasing funding for geriatric mental health initiatives, we can better serve older adults and provide them with the support they need.