Bile imbalance liver cancer is emerging as a critical area of research that links the disruption of bile acids produced by the liver to severe liver diseases, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent type of liver cancer. A recent groundbreaking study highlights how this imbalance, alongside impairments in bile acid metabolism, can promote the development of HCC through a complex molecular mechanism involving the YAP FXR signaling pathway. With bile acids serving not only to aid fat digestion but also to regulate various metabolic functions, understanding their role in liver cancer treatment becomes paramount. As researchers uncover the significance of bile acid regulation, new therapeutic interventions are being considered, offering hope for improved outcomes in liver cancer patients. Delving into the interplay between bile imbalance and liver cancer may open new avenues for effective treatments and preventive strategies.
The phenomenon of disrupted bile acid homeostasis is increasingly recognized as a significant factor in the progression of liver malignancies, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This condition can be described as a consequence of metabolic derangements in bile acids, impacting liver function and health. Enhanced understanding of bile acid signaling and its effects on liver cancer can pave the way for innovative approaches in liver cancer therapy. Researchers are particularly focused on the interactions within the Hippo/YAP pathway, which plays a vital role in regulating cell growth and metabolic processes. Investigating these complex relationships not only broadens our comprehension of liver pathology but also contributes to effective liver cancer treatment strategies.
Understanding Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer
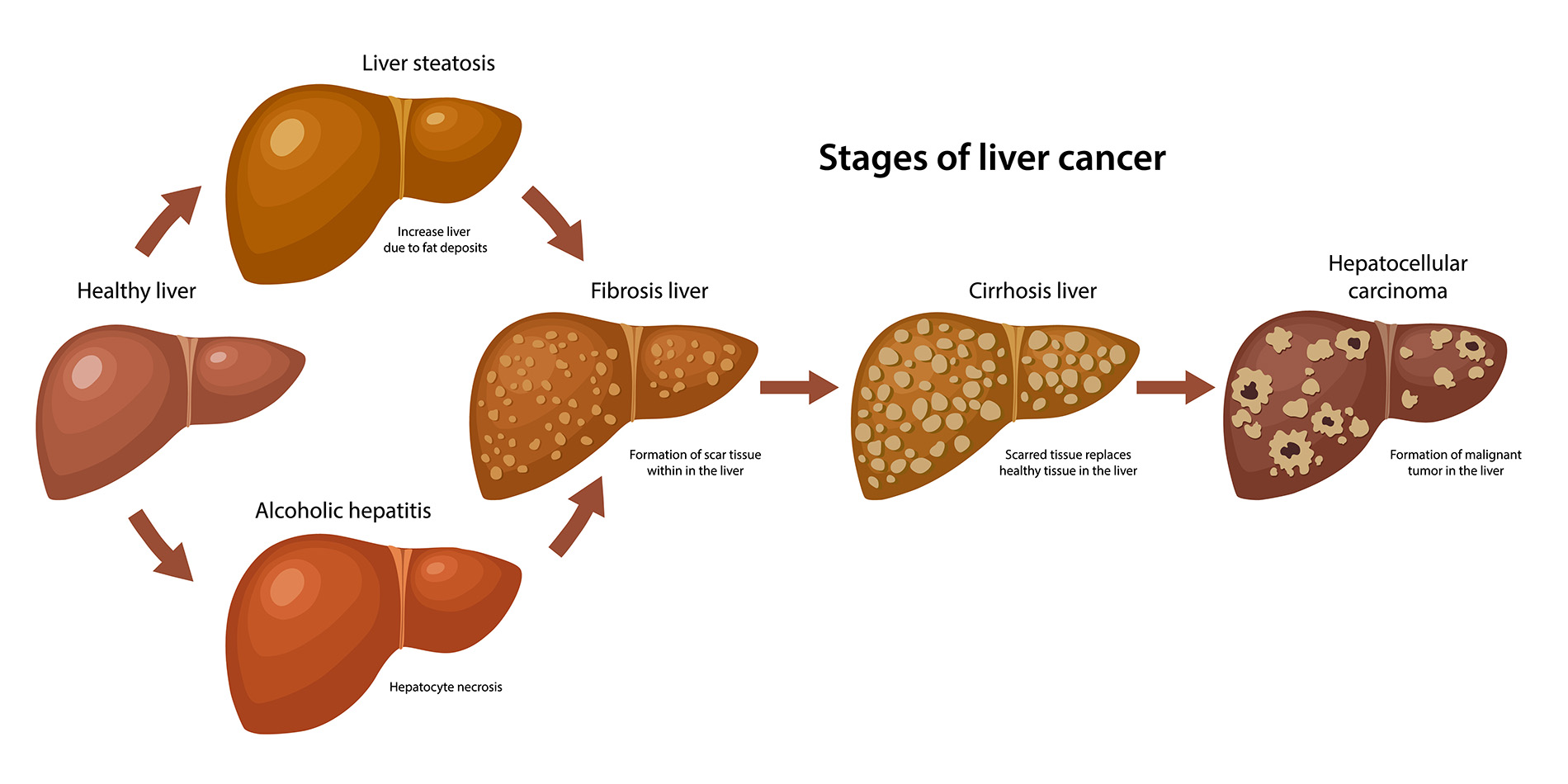
Bile imbalance is increasingly recognized as a significant factor contributing to the development of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). When the liver fails to regulate bile acids properly, it can lead to an excess that promotes inflammation and cellular damage. This process creates a biochemical environment in which cancerous cells can thrive. The relationship between bile metabolism and liver cancer underscores the need for a deeper understanding of physiological processes, as highlighted by recent studies that have unveiled critical molecular pathways involved in these interactions.
The research indicates that disruptions in bile acid regulation can activate oncogenic pathways, leading to the formation of tumors. Specifically, the study points to the role of YAP (Yes-associated protein), which modulates bile acid metabolism by inhibiting FXR (Farnesoid X receptor). With excessive bile acids in the liver, the risk of cell transformation into malignancies rises significantly. Thus, managing bile acid levels could be a pivotal aspect of treatment strategies aimed at reducing liver cancer risk.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is bile imbalance and its connection to liver cancer?
Bile imbalance refers to the disruption in the normal production and regulation of bile acids, which are essential for fat digestion and metabolic processes. Research has shown that this imbalance can lead to liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common type of liver cancer. Key molecular mechanisms, such as the role of YAP in inhibiting FXR function, contribute to increased bile acid accumulation in the liver, which may lead to inflammation and tumor development.
How does bile acid metabolism influence liver cancer treatment options?
Bile acid metabolism is crucial in understanding liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The disruption of this metabolism can result in liver damage and cancer progression. Targeting the pathways that regulate bile acid production, such as enhancing FXR function or promoting bile acid excretion, offers potential treatment options. Researchers are exploring pharmacological solutions that stimulate bile acid homeostasis to prevent liver cancer.
What role does YAP play in bile imbalance and liver cancer?
YAP (Yes-Associated Protein) plays a significant role in bile imbalance related to liver cancer by acting as a repressor of FXR (Farnesoid X receptor), essential for maintaining bile acid homeostasis. The activation of YAP can lead to overproduction of bile acids, resulting in fibrosis, inflammation, and ultimately hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Thus, inhibiting YAP’s repressive effects may provide a therapeutic avenue for treating liver cancer.
How can the FXR signaling pathway provide insights into liver cancer therapies?
The FXR signaling pathway is vital in regulating bile acid homeostasis. Disruption of this pathway, particularly through YAP inhibition, can lead to liver injury and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). By enhancing FXR signaling or blocking pathways that enable YAP’s repressive functions, new liver cancer therapies can be developed. Current research is focusing on pharmacological agents that stimulate FXR to mitigate bile imbalance and its consequences.
What are the implications of bile acids as hormones in liver cancer research?
Bile acids, beyond their digestive function, act as hormones regulating metabolic processes. Their role in liver cancer research is becoming increasingly recognized, particularly concerning hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Understanding how bile acids influence cell signaling and metabolism can lead to innovative treatment strategies. Research indicates that targeting bile acid metabolism and its hormonal effects may open doors to new therapeutic options for managing liver cancer.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer | A critical imbalance in bile acids can trigger liver diseases, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a common liver cancer. |
| Research Insights | Study identifies a key molecular switch that regulates bile acid production, revealing potential treatment avenues. |
| Role of the Liver | The liver produces bile, which digests fats and regulates metabolic processes. |
| YAP and FXR Interaction | YAP inhibits the FXR receptor, leading to bile acid overproduction, fibrosis, inflammation, and cancer. |
| Potential Treatment Strategies | Blocking YAP’s effects or stimulating FXR function may reduce liver damage and cancer progression. |
| Research Significance | The findings could lead to pharmacological solutions targeting FXR and improving liver health. |
Summary
Bile imbalance linked to liver cancer is an emerging area of research that highlights the critical role of bile acids in liver health. Recent studies have uncovered how disruptions in bile acid metabolism can lead to severe consequences, including the onset of liver diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma. By understanding the molecular underpinnings of bile production and regulation, researchers are paving the way for potential therapeutic interventions to combat liver cancer effectively.